How Do Different Countries’ Economies Compare?
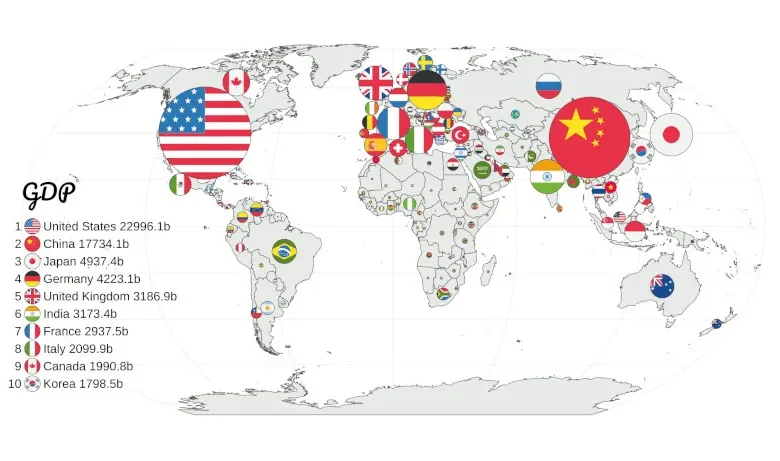
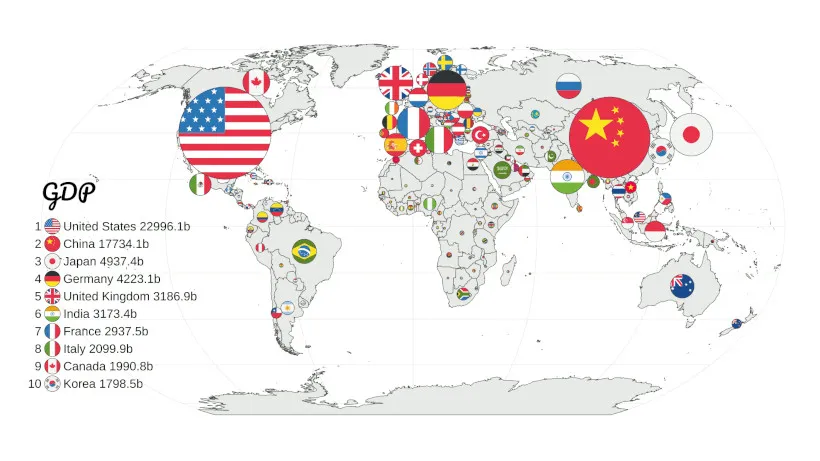
The size, composition, and performance of economies vary greatly throughout the world. Thanks to their sophisticated businesses and services, countries like the US, China, and Germany have some of the highest GDPs.
In the meantime, population growth and the expansion of industrial bases are driving the rapid rise of emerging countries like Brazil and India. Economic performance is greatly influenced by elements such as trade alliances, technological developments, and natural resources.
Manufacturing is a top priority for certain nations, while financial services and agriculture are priorities for others. Metrics like GDP, per capita income, and trade balances are used to compare economies, demonstrating the diversity of economic strengths and developmental phases across the world.
1. The Top Economies in the World
- The US economy is the biggest in the world, propelled by cutting-edge services, technology, and a robust customer base.
- China is a fast-growing economy that prioritizes exports, manufacturing, and technology.
- Japan is renowned for its strong electronics and automotive sectors as well as for technological innovation.
- Germany is the biggest economy in Europe and is well-known for exporting industrial and engineering goods.
- India’s economy is expanding quickly because to services, technology, and a youthful labor population.
- The UK has a diversified economy with robust service and financial industries.
- France is fueled by innovative industries, luxury goods, and agriculture.
- Italy is renowned for its tourism, luxury goods, and manufacturing industries.
- Brazil: Known for its natural riches and agriculture, this country has the biggest economy in South America.
- Canada: Rich in technology, natural resources, and a sound financial system.
2. What Country Has the Smallest GDP?
The tiny Pacific island nation of Tuvalu has the lowest GDP. The economy of Tuvalu is one of the smallest in the world, with an estimated GDP of about $70 million. Subsistence farming, fishing, remittances from citizens employed overseas, and income from its internet domain extension (.tv) are the main drivers of its economic activity. Its economic growth is further hampered by its geographic remoteness, scarcity of natural resources, and susceptibility to climate change.
3.Converting Currencies with Exchange Rates
Converting Currencies with Exchange Rates
Currency conversion is the process of exchanging one country’s currency for another using a specified exchange rate. The amount of one currency that is equal to another is shown by the exchange rate. For example, if the USD/EUR rate is 0.85, it means $1 equals €0.85.
Steps to convert currencies:
- Know the exchange rate: Check real-time rates through banks, forex platforms, or currency converters.
- Determine the amount: Multiply the amount in the base currency by the exchange rate to get the converted value.
- Account for fees: Be aware of transaction fees or margins added by banks or exchange services.
Currency fluctuations, driven by factors like interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events, can impact conversion values significantly. Use tools like online calculators or financial apps to simplify the process.
Conclusion:
Comparing the economies of different countries is a complex task, influenced by various factors such as population size, natural resources, technological advancements, government policies, and global economic conditions. While GDP and GDP per capita are essential metrics, they provide only a partial picture. To gain a more comprehensive understanding, it’s crucial to consider factors like income inequality, human development index, and quality of life.
As the global economy continues to evolve, so too will the economic landscapes of individual countries. Emerging economies, particularly in Asia and Africa, are increasingly playing a significant role in the global economy. However, developed economies continue to dominate in terms of technological innovation and financial influence.
FAQs:
1.Which nation boasts the world’s biggest economy?
The market worth of all finished goods and services produced inside a nation’s boundaries over a given time period is expressed in monetary terms as the GDP, or gross domestic product.One It is a crucial sign of the state of a country’s economy. We can determine the relative economic size, growth rates, and prospects for future development of various nations by comparing their GDPs.
2. How Do Different Countries’ Economies Compare?
Countries’ economies vary significantly in size, growth rates, and structure. Economic comparisons often rely on metrics like Gross Domestic Product (GDP), GDP per capita, and purchasing power parity (PPP). The United States leads as the largest economy globally, fueled by its technology and financial sectors. China follows closely, driven by manufacturing and exports. Smaller economies like Luxembourg excel in GDP per capita due to financial services and niche industries.
3. Why do exchange rates affect international economic comparisons?
Exchange rates affect international economic comparisons because they determine the relative value of one country’s currency against another’s. A country with a strong currency may appear wealthier compared to others when comparing GDP, but this doesn’t always reflect its true economic power. For example, fluctuations in exchange rates can make imports cheaper and exports more expensive, affecting trade balances and economic competitiveness.
4. How do countries with smaller economies compete globally?
Countries with smaller economies compete globally by focusing on strategic sectors where they can outperform larger economies. They often specialize in niche markets, such as high-end luxury goods, advanced manufacturing, or specialized services. For example, Switzerland has become a global leader in finance, pharmaceuticals, and precision engineering, while Singapore excels in technology and trade due to its strategic location and business-friendly environment. These nations also invest in education to cultivate highly skilled workforces, further enhancing their competitiveness.