Diabetes types and treatments
1. Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune condition known as type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system targets and kills the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, a hormone that controls blood sugar levels. It is usually diagnosed in youth and young adults.
Type 2 Diabetes
Kind 2 diabetes is the most common kind. 2. This causes either an aberrant insulin response by body cells or insufficient insulin synthesis by the pancreas. It is usually found in older adults and is caused by lifestyle and food choices.
Gestational Diabetes
Cause: pregnancy-related hormonal changes that impact insulin utilization.
Key Features: Usually goes away after childbirth, although it raises the risk of Type 2 diabetes in the future. It occurs in pregnant women.

2. Diabetes Symptoms
Typical signs of diabetes include:
1. frequent urination.
2. Increased thirst
3. Extreme hunger
4. Fatigue
5. Blurred vision
6. Slow-healing wounds
7. Unexplained weight loss
8. Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
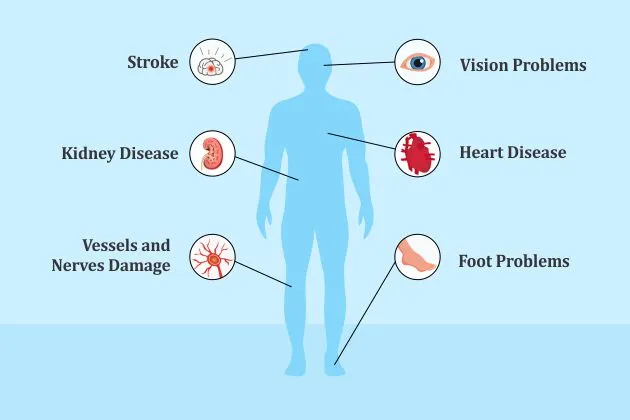
Depending on the type of diabetes (Type 1, Type 2, or gestational diabetes), these symptoms might appear gradually or all at once. Diabetes can cause major consequences if it is not managed; therefore, early detection and care are crucial.
3. Treatment of diabetes
Diet
a well-rounded diet that prioritizes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while reducing processed foods, sugary beverages, and saturated fats.
Exercise
Exercise is essential for diabetes management because it lowers the risk of complications, increases insulin sensitivity, and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Frequent exercise, such as swimming, cycling, or walking, improves the body’s capacity to use insulin efficiently, which lowers blood sugar levels. Additionally, it lowers stress, enhances cardiovascular health, and aids with weight management. To prevent sharp swings, it’s critical for diabetics to check their blood sugar levels both before and after exercise.
weight
Controlling one’s weight is crucial for diabetes, especially for those with Type 2 diabetes. Keeping a healthy weight decreases blood sugar, improves insulin sensitivity, and lowers the risk of problems like heart disease. A balanced diet and consistent exercise can help you lose weight and improve blood sugar regulation.
Type 1, Diabetes
controlled by controlling blood sugar levels with insulin shots or an insulin pump. Exercise, a balanced diet, and routine blood glucose testing are also crucial.
Type 2 diabetes
frequently managed with lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss, regular exercise, and a balanced diet. Blood sugar can be controlled with oral drugs like metformin, and in more severe cases, insulin may be needed.
Gestational Diabetes
controlled by blood sugar monitoring, exercise, and a nutritious diet. If lifestyle modifications are unable to regulate blood sugar levels, insulin may be required.
4. Benefits of Buying Health Insurance for Diabetic Patients
Purchasing health insurance for people with diabetes has several benefits, including lowering financial burden and guaranteeing access to essential medical care. Insulin and oral pills, which can be costly without coverage, are among the diabetes-related treatments that health insurance helps pay for. Additionally, it gives access to routine health examinations, blood tests, and screenings—all of which are essential for keeping an eye on blood sugar levels and averting issues.
Health insurance covers the costs of hospital stays, procedures, and doctor visits in the event of an emergency or complications that require hospitalization.
Conclusion
To sum up, diabetes may be controlled, but it needs constant attention and care. As an autoimmune disease, type 1 diabetes usually necessitates lifetime insulin treatment. Type 2 diabetes, often influenced by lifestyle factors, can be managed with lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes insulin. Pregnancy-related gestational diabetes usually goes away after delivery, but it needs to be closely watched during pregnancy.
Regardless of the kind, blood sugar monitoring, consistent exercise, and a nutritious diet are crucial elements of treatment. People with diabetes can live active, healthy lives and reduce their risk of complications with the correct management strategy.
FAQs
1. Can diabetes be cured?
Diabetes cannot be cured at this time. However, with the right medications, lifestyle changes, and consistent observation, it can be effectively treated. Because the body is unable to make insulin, people with Type 1 diabetes must receive insulin therapy for the rest of their lives.
2. Can exercise help in managing diabetes?
Indeed, exercise has a significant role in diabetes management. Frequent exercise increases insulin sensitivity, which enhances the body’s ability to use insulin. Additionally, it reduces blood sugar levels by promoting the muscles’ absorption of glucose for energy. Exercise improves cardiovascular health, lowers stress, and helps manage weight—all of which lead to better overall diabetes control.
3. How is type 2 diabetes treated?
Weight control, frequent exercise, and a nutritious diet are all part of the treatment for type 2 diabetes. Insulin therapy may be required in certain situations, and medications like metformin may be recommended.
4. What is the treatment for gestational diabetes?
In order to control blood sugar levels, gestational diabetes is usually treated with lifestyle modifications, such as eating a balanced diet and exercising frequently. Monitoring blood sugar is crucial, and insulin injections or oral drugs may be recommended if lifestyle modifications are insufficient to maintain appropriate levels.



