How Friday’s Jobs Report Can Signal a Coming Recession
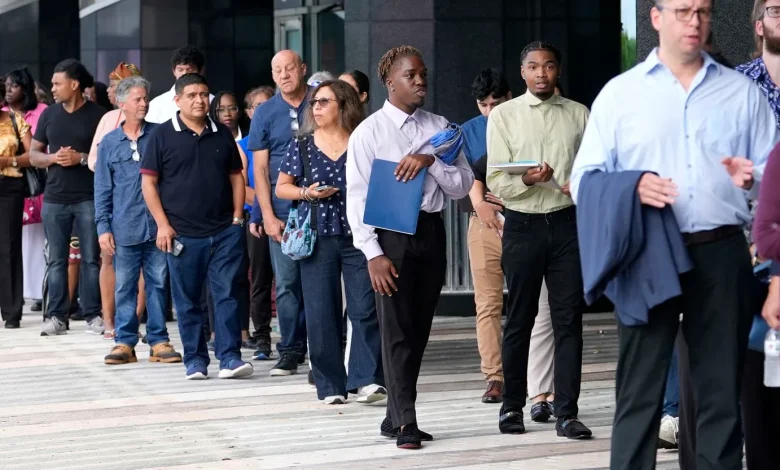

One important economic indication that may portend a possible recession is Friday’s jobs report, particularly if it reveals an increase in unemployment.
The Sahm Rule, a trustworthy indicator of a recession, is activated whenever the unemployment rate rises by more than 0.5% from its most recent low, according to economists who keep a careful eye on it.
Because it may have an impact on interest rate decisions and market sentiment generally, the Federal Reserve and investors are especially interested in this data. A notable shift in employment levels could be an indication of economic cooling, which could lead to rate reductions or raise questions about the state of the economy.
Some key indicators to watch
Hours worked: One indicator of the state of the economy is the duration of the typical workweek. Before taking more serious measures, firms usually reduce hours if demand declines. In July, the average workweek decreased little from 34.3 to 34.2 hours.
Labor force movement: Although it raises the unemployment rate, the number of people returning to the workforce to seek employment reflects underlying opinion regarding the health of the labor market.
Temporary layoffs: In an investor note released Wednesday, Bank of America economists noted that a portion of the increase in July unemployment was due to a surge in temporary layoffs, which was the third-largest since 2000 (not including COVID). These “could turn permanent,” the economists warned. They did, however, note that the spike was probably caused by the “summer auto retooling-related volatility in Michigan” and that they anticipate this tendency to have been reversed in the August report.
Impact of weather: The BLS stated in the July jobs report that Hurricane Beryl “had no discernible effect” on the country’s unemployment and employment statistics.However, the weekly jobless claims datahas revealed some rises in joblessness, especially in Texas, Mike Skordeles, Truist’s head of US economics, told CNN.“We know that there were distortions there,” he said.
The job market usually experiences severe difficulties during a recession as companies cut back on hiring, lay off employees, or shut down operations to save money.
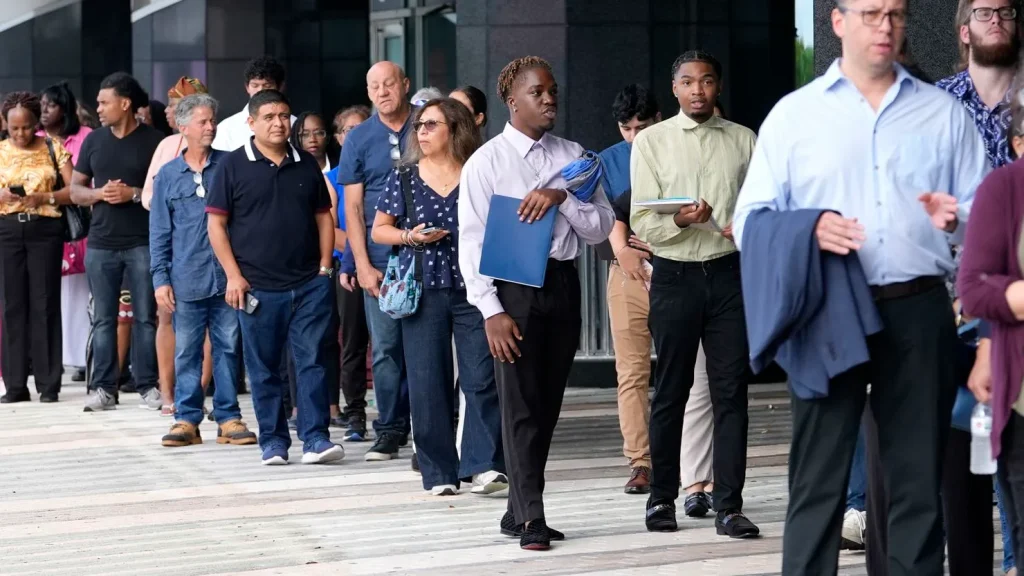

1. recession job market
Job security and unemployment rates frequently increase, particularly in industries like manufacturing, retail, and hospitality that are vulnerable to economic downturns. Part-time or gig work may become more prevalent in the labor market as businesses look for flexible hiring options.
Job seekers may encounter intense competition for a small number of possibilities, and wage growth tends to stall. But in the midst of a wider economic downturn, some industries, such as healthcare, technology, and critical services, might hold up or even expand.
2 . Jobs report: A spike in unemployment might signal a recession, according to the rule, but probably not this time.
The latest jobs report indicates a rise in unemployment, which could traditionally signal a potential recession under the Sahm Rule—a rule that predicts a downturn if unemployment increases by 0.5% from its recent low.
However, analysts suggest this may not be the case this time. Despite the uptick, other economic indicators such as consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic resilience point to continued growth.
The unique post-pandemic economic conditions, including robust labor market adjustments and ongoing wage growth, indicate that the economy may avoid a recession despite historical warning signs
3. Which business has less competition?
Companies in nascent industries or niche markets, where demand is increasing but major companies have not yet taken control, tend to have less competition.
Specialized local services like artisanal food goods, eco-friendly cleaning, or individualized wellness coaching are a few examples. Furthermore, businesses that use cutting-edge technology, such as blockchain solutions tailored to particular sectors or sustainable product breakthroughs, frequently face fewer early-stage rivals.
However, a solid grasp of client needs, distinct distinctiveness, and extensive market research are necessary for success in these industries. There are benefits to operating in less competitive areas, but there are drawbacks as well, such as the difficulty of educating customers and building confidence in novel products.
Conclusion:
Fears of a recession have been heightened by the recent jobs report, but it’s important to take the larger economic picture into account. The Sahm Rule is a good indicator, but it’s not infallible. The future course of the economy will also be greatly influenced by other elements, including governmental regulations and worldwide economic trends.
To determine the probability of a recession, it’s critical to remain informed and keep a careful eye on economic indicators.
1. How does the jobs report signal a recession?
A rise in the unemployment rate by 0.5% or more over the past 12 months can trigger the Sahm Rule, a reliable recession indicator. It suggests that the economy is likely already in a recession if joblessness significantly increases, as businesses may cut jobs due to economic slowdown.
2.What is the Sahm Rule, and why is it important?
One economic metric that predicts the onset of a recession is the Sahm Rule. Claudia Sahm, an economist, developed it in 2019. According to the rule, when the national unemployment rate’s three-month moving average increases by 0.50 percentage points or more from its low over the preceding 12 months, a recession is probably already under way.
3. What are other indicators besides the jobs report that predict a recession?
Aside from the unemployment rate, other signs of a possible economic slowdown include the inverted yield curve, a drop in consumer confidence, and a decrease in company investment. Predictions of a recession are now more questionable, though, as these indicators have recently sent conflicting signals.