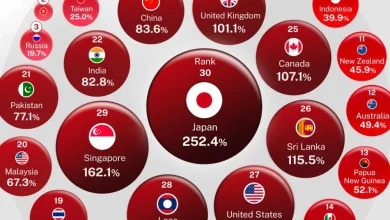
How to Understand Economic Rankings: A Simple Guide
Economic rankings are essential tools for evaluating the performance, strength, and competitiveness of countries in the global economy. They offer insight into various economic indicators that help policymakers, investors, and businesses make informed decisions. To fully grasp these rankings, it’s important to understand the key metrics they rely on and how they reflect a country’s economic position.
Basics of Economy
Choice and Scarcity: Human desires are limitless, while resources (land, labor, and capital) are finite. Economics is the study of how people and communities decide how best to divide up these limited resources.
Equilibrium occurs when supply and demand are equal.
Economies Types:
1. Market economy: Prices, supply, and demand determine decisions with little help from the government (e.g., the U.S.).
2. Command Economy: Most economic decisions are made by the government (e.g., North Korea).A mixed economy, such as many contemporary economies, combines aspects of both market and command economies.
3. Economic Measures: An economy’s whole output is measured by its gross domestic product, or GDP.Rising prices are reflected in inflation, which has an impact on purchasing power.
The percentage of persons who are actively looking for work but are unsuccessful is tracked by the unemployment rate.
4. Government Role: In order to foster stability, growth, and equity, governments control economies by establishing laws pertaining to trade, taxation, expenditures, and interest rates.
1. What is the largest economy in the world?
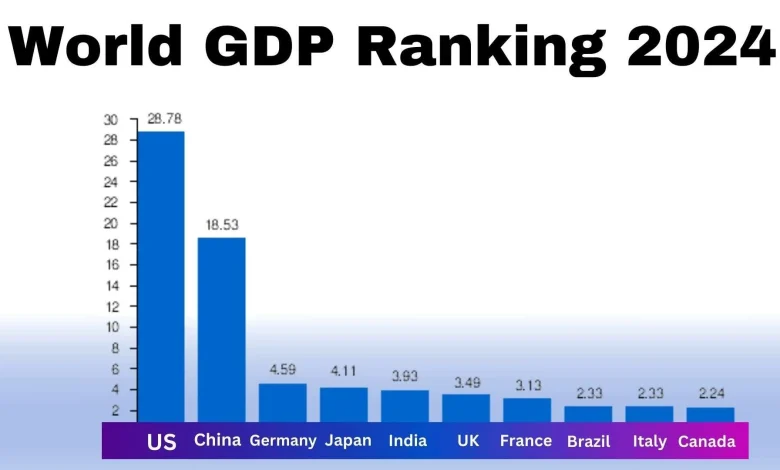
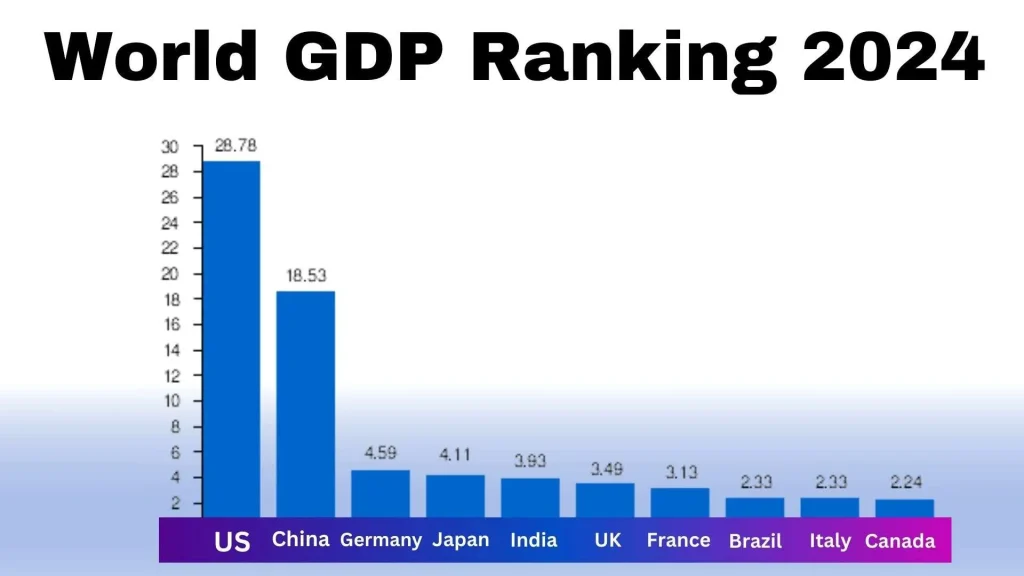
The United States of America has the largest economy in the world, with a GDP of over $20 trillion. China is on the verge of becoming the largest economy because it keeps making significant investments in economic expansion. The United Kingdom, Germany, and India are among the other prominent countries that come next. See the list below to find out which countries have the highest GDPs:
1. United States
In terms of nominal GDP, the US economy is the biggest in the world. The economy’s service sector, which encompasses real estate, insurance, healthcare, professional and commercial services, and finance, is the largest contributor to that GDP.7.
Foreign direct investment and flexible business investment are made possible by the comparatively open economy of the United States. It is the world’s leading geopolitical force and, as the creator of the principal reserve currency, is able to sustain a sizable external national debt.8910
Council on Foreign Relations. “The Dollar: The World’s Reserve Currency.”
2. China
China has the greatest PPP and the second-largest nominal GDP in current USD worldwide. Due to its economy’s remarkable expansion during the past 20 years, some analysts have theorized that China’s economy could eventually surpass that of the United States as the largest in the world.
Over the past 40 years, China’s economy has gradually opened up, leading to significant advancements in both economic growth and living standards. Trade and investment have flourished both domestically and internationally as a result of the government’s progressive phase-out of collectivized agriculture and industry, improved market price flexibility, and enhanced company autonomy.
3. Germany
Germany ranks as the world’s third-largest economy in 2024, with a GDP of approximately $4.6 trillion. Known for its robust industrial base, Germany excels in automotive, engineering, and chemical sectors. Its economy thrives on exports, driven by precision manufacturing and innovation. Despite slower growth compared to emerging markets, Germany remains a powerhouse in Europe due to its skilled labor force, advanced infrastructure, and commitment to research and development.
4. Japan
Under the policies of former Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, Japan has experienced a recent uptick in growth following the Lost Decade of the 1990s and the effects of the global Great Recession. Nevertheless, the country lacks natural resources and is reliant on energy imports, particularly after the 2011 Fukushima disaster caused its nuclear power industry to shut down completely. A rapidly aging population has also been a problem for Japan.
5. India
With a GDP of almost $3.9 trillion in 2024, India would have the fifth-largest economy in the world. Important industries like manufacturing, services, agriculture, and information technology are responsible for its quick expansion. India’s dynamic domestic market is facilitated by its sizable, youthful workforce and expanding middle class. Technological developments and strong private consumption also contribute to the nation’s economic growth.
2. Which economy in the world is expanding the fastest?
Guyana is expected to have the world’s fastest-growing economy in 2024, with an impressive GDP growth rate of about 33.9%. This remarkable increase is mostly attributable to the nation’s expanding oil and gas sector, which has been fueled by major offshore finds made by ExxonMobil and its partners in the Stabroek Block.
These findings have significantly boosted Guyana’s economy and made it a major player in the world energy market. The government’s diversification initiatives and infrastructural improvements have also improved growth prospects.
Macao, which is recovering with a projected growth rate of 13.9% due to the resurgence of its casino sector and increasing private investment, and Niger, which is forecast to grow by 10.4% due to new oil exports through a large pipeline project, are two other significant rapidly rising economies. These illustrations demonstrate how resource-driven industries and wise investments may greatly strengthen national economies.
Conclusion:
Final Thoughts: Comprehending Economic Rankings
By contrasting variables like GDP, GDP per capita, and growth rates, economic rankings offer important insights into a nation’s economic health and progress. These rankings illustrate the economic standing of countries globally, assisting individuals, corporations, and policymakers in making well-informed decisions.
Even though GDP is the most widely cited indicator, a full picture of a country’s economic health requires taking into account other elements like inflation, income disparity, and quality of life. A greater understanding of the dynamics of the global economy and the forces influencing changes in national economies is made possible by knowing how these rankings are determined and what they mean.
FAQs:
1. What is the rank of India in world GDP?
As of 2024, India ranks as the fifth-largest economy in the world by nominal GDP, with a GDP of around $3.9 trillion. This remarkable position highlights India’s rapid economic growth, driven by its booming information technology sector, robust domestic market, and increasing industrialization. India’s economy has been expanding due to a young population, increased foreign investment, and a growing middle class. While it is still behind major global players like the U.S., China, Japan, and Germany, its continued economic momentum suggests that India may rise further in global rankings in the coming years.
2 . Why is GDP the most commonly used measure in economic rankings?
GDP is widely used because it provides a comprehensive snapshot of a country’s economic activity by summing the value of all goods and services produced within a given period. It serves as a standard benchmark for comparing the size and performance of different economies.
3. What is the evolution of rankings?
Economic growth rates, changes in the value of the currency, inflation, governmental reforms, and technical breakthroughs are some of the reasons that cause fluctuations in economic rankings. Because of their quick industrialization and investment, emerging markets frequently rise in the rankings, whereas more established economies could grow more slowly.