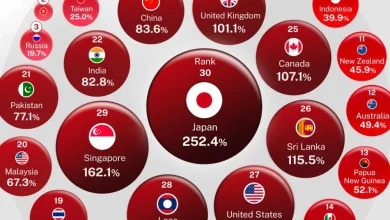
What Factors Affect Home Price-to-Ease Ratio by State?

A number of factors, such as income levels, housing demand, and supply, affect the home price-to-ease ratio by state. Higher ratios are frequently seen in states with thriving labor markets or well-liked metropolitan areas because of rising demand and constrained housing supply.
States with weaker economic growth or those in rural areas, on the other hand, can have lower percentages because property prices are still lower there. Property taxes, mortgage rates, municipal real estate regulations, and demographic trends like in-migration or out-migration are further significant factors.
Elevated ratios are frequently seen in areas with more stringent zoning regulations or more expensive development, which indicates difficulties in increasing the supply of housing to meet demand.
1.The Top Factors Affecting House Prices
Several factors influence house prices:
- Interest Rates: Mortgages become more affordable when interest rates are lower, which increases demand and may drive up prices. Higher interest rates, on the other hand, have the potential to reduce demand and impede price increases.
- Supply and Demand: Prices are greatly impacted by the equilibrium between the supply of available properties and buyer demand. While an overabundance of housing might result in price decreases, a scarcity can raise costs
- Location: A location’s appeal, particularly its closeness to facilities, educational institutions, transit, and employment prospects, affects costs. Prices are typically higher in prime locations.
- Government Policies: The affordability and costs of housing can be impacted by government policies such as tax breaks, zoning laws, and housing subsidies.
- Demographics: The demand for and cost of housing can be impacted by factors such as household size changes, aging populations, and population expansion.
- Inflation: Over time, inflation can reduce purchasing power and raise the cost of housing.
- Market Sentiment: Housing prices may be impacted by investor confidence and market sentiment. Prices can rise in response to positive mood and fall in response to negative sentiment.

2. Factors that affect the housing market
The status of the economy, interest rates, real income, and shifts in population size all have an impact on the housing market. In addition to these demand-side variables, supply will also affect home prices.
Economic growth. Housing demand is influenced by income. People will be able to spend more on homes as a result of increased economic growth and incomes, which will raise demand and drive up prices. In reality, it is frequently observed that the demand for housing is income elastic (luxury product), meaning that as incomes rise, a larger percentage of income is spent on housing.
Interest rates. Monthly mortgage payments are impacted by interest rates. High interest rates will make mortgage payments more expensive and reduce demand for home purchases. When borrowing rates are high, renting is comparatively more appealing than owning.
Consumer confidence. When deciding whether or not to take on the danger of getting a mortgage, people’s confidence is crucial. Expectations regarding the property market in particular are crucial; if individuals are afraid that home values may decline, they will put off purchasing.
3. Will property prices fall in 2024 in India?
The property prices in India are unlikely to see a significant fall in 2024 due to various factors. The real estate market remains robust, with steady demand for residential properties, particularly in urban areas. Increased urbanization, population growth, and government initiatives like “Housing for All” continue to boost demand, especially in affordable housing segments.
However, rising interest rates might impact affordability for some buyers, potentially slowing down demand in certain segments. Developers are also expected to maintain price stability due to increased construction costs and limited inventory in key markets.
While some minor corrections in specific regions are possible, the overall outlook for the Indian real estate market in 2024 suggests continued growth and resilience rather than a widespread price decline.
Conclusion:
The Home Price-to-Ease Ratio is a crucial metric for understanding housing affordability in different states. A variety of factors, including economic conditions, housing supply and demand, interest rates, local regulations, cost of living, and state and local taxes, influence this ratio.
By analyzing these factors, individuals can gain insights into the affordability of housing in specific states and make informed decisions about homeownership.
FAQs:
1. What is the Home Price-to-Ease Ratio?
The Home Price-to-Ease Ratio is a measure of housing affordability. It compares the median home price to the median household income in a given area. A higher ratio indicates that homes are more expensive relative to local incomes, making housing less affordable, while a lower ratio suggests better affordability.
2. How Does the Ratio Vary Across States?
States’ median home prices, median earnings, housing supply, and local economic conditions all affect the Home Price-to-Ease Ratio. Higher ratios are typically found in states with lower salaries or higher home costs, which makes housing less affordable. On the other hand, states with higher salaries and more reasonably priced homes tend to have lower ratios, which suggests better affordability.
3. How does the cost of living impact this ratio?
The cost of living impacts the home price-to-income ratio by affecting both housing prices and household earnings. In high-cost areas, housing prices often increase faster than wages, leading to a higher ratio and less affordability.